Our Federal, State and Local Governments Have Failed Us All, Big Time, on Human Caused Global Warming, the Many Increasingly Severe and Costly Extreme Weather Events Occurring this Century Already, and Projected to Continue Worsening Global Warming Impacts, Which Will Especially Affect Every Child Living Today, and Every Other Creature that Lives on the Surface Now and in the Future
Our country’s and other countries’ federal, state and local governments continue to be negligent by not sufficiently taking on the necessary actions to bring human-caused global warming and the countless impacts of global warming caused climate changes, extreme and dangerous weather occurrences, rising and changing oceans, lakes, rivers and the many regions of the world. Concerted and effective actions by all citizens of the world that will bring about the necessary reductions in emissions from all people, businesses, organizations, institutions and governments to protect all who live on Earth and future inhabitants of Earth. The actions are already late. However, the adage that such actions are “better late than never” most certainly applies since to continue adding to the already accumulating volume of those gases in Earth’s biosphere (atmosphere and water bodies) is most definitely going to amplify the negative and increasingly dangerous physical,social and economic changes to our world and planet.
A famous civil rights leader, who lived in the last century and who’s birthday is celebrated every January in the United States, and recognized as an official U.S. holiday, once said: “the time is always ripe to be right” (Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr.). That is equally applicable to everyone fighting global warming by reducing their daily, monthly and annual greenhouse gas emissions to a flat minimum, and without anymore delay!
Global Warming is a Local, State, National and International Emergency that Will Only Worsen in Time, Not Get Better
Unfortunately, as the volumes of greenhouse (heat-trapping) gases that are being released to the atmosphere on a daily basis as a result of human activity (mainly from burning coal, natural gas, oil and jet fuel) continue to accumulate there; and Earth’s remaining green space (forests, prairies and other carbon dioxide (CO2) consuming (sequestering) vegetation) is reduced; and Earth’s oceans, seas, the Great Lakes and numerous other water bodies become evermore warmer and saturated with carbon dioxide (CO2), making them more acidic; the prospect of Earth being as hospitable as for life as it has been in the recent millennia in which humans have inhabited this planet is getting slimmer and slimmer.
Scientific studies have been showing for decades, and now with more and more clarity, that modern day living – particularly by residents in the developed countries of the world, who rely so heavily on burning fossil fuels in their daily living – for energy warmth in winter, and electricity generation and transmission, year-round, for shipping goods and trading, and, moreover, for personal or work related travel, the construction, pavement and land alterations that are done which not only allow for that activity, but promote it, that that kind of living by so many millions and even billions of people, will ultimately lead to grave consequences for our planet.
And with our human population continuing to grow geometrically, coupled with the outright refusal of much of the population, their political leaders, and even the recently elected president of our United States of America, Donald J. Trump, continuing to advocate for the highly resource consumptive “business as usual” lifestyle — many human and other lives have already been lost, and people all over the world have suffered, and many more people and animals living in the future will suffer, or be lost, and many trillions of dollars will be lost as well as a result of climate change related “natural” disasters, and rising sea level, a situation which now is not only unprecedented but becoming increasingly dire and predictable.
It’s not like you can just turn the water faucet off and global warming will stop. As stated in Gavin Schmidt and Joshua Wolfe’s comprehensive textbook: “Climate Change – Picture the Science” (2008), it could take centuries and even millennia to reverse it. “even if we act to keep atmospheric concentrations at the same level they are now [atmospheric CO2 concentrations 400 parts per million], the global mean temperature will continue to increase for a few decades as a result of past greenhouse gas emissions [GHGs] and the thermal inertia of the oceans [Water holds heat and releases it much slower than hard surfaces such as cement and asphalt.]”
All we can do now is to slow the pace of global warming by conserving energy obtained either directly or indirectly from burning fossil fuels. Moreover, changing to energy alternatives that don’t add to the rising concentrations of GHGs takes more time and money [but creates more long term jobs], and finding ways to adapt to the changes in the climate and the effects brought about by those changes will also cost money and will hurt the poor and the very young and the more elderly individuals [very young have less body mass to buffer individuals to higher heat; older persons are more susceptible to heat stroke].
“In short, there are no shortcuts to addressing a challenge that is global, pervasive, profound, and long term. Global citizens must grasp the challenge, master its intricacies, and take responsibility, for our own generation, and those to come”.[Jeffrey D. Sachs, New York, 6/16/2008]
Also see “UW-Madison Faculty Challenge DNR Climate Change Revisions”.
The following is from Lee Bergquist of the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel, January 22, 2017:
In a shift from the practice of two other state agencies, Wisconsin emergency management officials have released new information on climate change and its implications for the state.
****
In a report that it posted online last week, the state Division of Emergency Management devoted extensive attention to climate change and how a warming planet could spur natural disasters such as floods, drought and forest fires.
The report contrasts with the Department of Natural Resources and the state Public Service Commission, which scrubbed mentions of climate change and human-generated greenhouse gases from their websites.
As recently as December, DNR officials removed language from a web page devoted to the Great Lakes that had earlier acknowledged the role humans play in global warming. Officials inserted new wording saying climate change is a matter of scientific debate [Not – true! Truthful scientists will tell you the scientific debate ended years ago. MTN]
The PSC, which regulates electric utilities, eliminated its web page on climate change at some point before May 1, the Milwaukee Journal Sentinel found recently. The scrubbed information included a link to former Gov. Jim Doyle’s task force report on global warming. The Democratic governor’s report in 2008 recommended that Wisconsin reduce the use of fossil fuels and rely more on renewable sources of power. The measures were never enacted.
In the cases of the DNR and the PSC, the information can still be found on the Wayback Machine, an online archive.
In a new five-year disaster preparedness plan, the Division of Emergency Management cites research such as from the Wisconsin Initiative on Climate Change Impacts. It shows global warming is likely to produce more extreme weather. Examples: more days of 90-degree-plus temperatures and more intense rain events.
Bursts of rainfall, the report said, could lead to natural calamities such as flooding, collapse of dams, sinkholes and lake bluff failures.
While other agencies have removed references to the role of human activities in global warming, officials at the Division of Emergency Management included such a statement.
“Although it is widely accepted by the scientific community that the observed changes in global temperatures are the result of human actions, there is considerable uncertainty about the impacts these changes will ultimately have,” the agency wrote.
The document also acknowledges “some debate about the cause of climate change,” but added that statewide temperatures have increased 1.1 degrees in the past 50 years and that more extreme weather events are likely.
The new planning document was approved in December by the Federal Emergency Management Agency, said Lori Getter, spokeswoman for the state Division of Emergency Management.
Wisconsin was one of the first states to complete a new plan. As part of the process, FEMA required states to consider potential climate effects, she said.
Reducing the Current Suicidal Rate of Global Warming and Planning for Adapting to Changing Climates Demands Review of Goals, Principles and Actions by World’s Past Leaders and the Movements and Demonstrations by the People Who Expressed their Demands for Change
Today’s Populations, Businesses and Governments Responsible for Ensuring and Prolonging Earth’s Beauty, Economic Potential, Safety, and Humane Conditions for All It’s People and Animals Ought Not Ignore Leadership, Inspirations, Dreams and Concerted Actions of Millions of People and Leaders Who Lived Before Us, or Are Still Amoung Us, for Help in Music Guidance, Leader
To be continued….
Alarming New Study Predicts Dangerous Sea Level Rise to Occur in Decades, Not Centuries

A new scientific study, released to the media Tuesday by the European Geoscience Union’s Journal of Atmospheric and Physics, has major media sources reporting “alarming” study predictions of sea level rise and extreme weather from global warming, “much faster” than the rate of rise predicted in the most recent report by IPCC scientists. The world’s governments are being urged to “speed up the transition to carbon-free energy.” (Slate, 3/22/16)
Last year was the hottest on record. This January was the hottest on record. This February was the hottest on record — when the northern hemisphere breached 2 degrees of average warming for the first time in human history. “Our planet’s temperature just reached a terrifying milestone.” (Slate, 3/12/16)
The study uses climate simulations, paleoclimate data and modern observations to infer that continued high fossil fuel emissions will cause a slowdown and eventually shutdown the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation and the Southern Meridional Oceanic Circulation, resulting in an increase in powerful storms and nonlinear sea level rise, rising up to several meters in 50–150 years.
The meridional overturning circulation is a system of surface and deep currents encompassing all ocean basins. It transports large amounts of water, heat, salt, carbon, nutrients and other substances around the globe, and connects the surface ocean and atmosphere with the huge reservoir of the deep sea. The circulation of ocean water has been found to play a central role in climate and climate variability. Historically, the focus of research has been on the North Atlantic Basin, a primary site where water sinks from the surface to depth, triggered by loss of heat, and therefore buoyancy, to the atmosphere. A key part of the overturning puzzle, however, is the return path from the interior ocean to the surface through upwelling in the Southern Ocean. This return path is largely driven by winds. It has become clear over the past few years that the importance of Southern Ocean upwelling for our understanding of climate rivals that of North Atlantic downwelling, because it controls the rate at which ocean reservoirs of heat and carbon communicate with the surface.
The authors of the new study claim that the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) “missed” reporting on these important changes in their latest IPCC report, which the 18 authors of the new study underestimates ice sheet melt and the IPCC’s models are too insensitive to accurately account for ocean waters mixing.
In a video abstract: “Ice melt, Sea Level Rise and Superstorms”, lead author and climate scientist Dr. James Hansen states that evidence from paleoclimate data, climate modeling, and modern observations show that the maximum level of global warming that was set at the Paris Climate Summit meetings in early December 2015 of 2°C global warming to be “highly dangerous” and that “We have a climate emergency and must slash CO2 emissions ASAP or irreparable harm to the climate will be done for succeeding generations”.
A Day to Remember – February 29, 2016
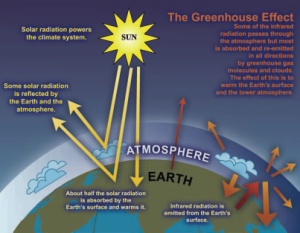
I could not allow this day – Feb. 29 – to pass without comment. Leap year – a year having an extra day in February – occurs only every four years.
So, is that good or bad?
It’s not good, in fact it’s DISASTROUS, because yet ANOTHER day, and year, and decade has gone by while our elected officials in the State of Wisconsin Legislature, and the U.S. Congress, and the population of our state and country, refuse to take the threat, and now reality, of global warming caused by too much fossil fuel burning – in cars, trucks, airplanes, electric power producing plants that burn fossil fuels, seriously, despite alarming increases in sea levels.
Too much fuel burning primarily coal, methane (natural gas), and oil products, have been burned by humans over the past decades and centuries for the energy that has been produced, resulting in the emission and accumulation of elevated concentrations of “greenhouse gases” in earth’s atmosphere, resulting in global warming, the rise in the elevation levels of earth’s oceans, due to the melting of the earth’s Arctic and Antarctic Circle’s land ice and snow, the shrinking of earth’s mountainous glaciers, a thawing of the earth’s permafrost region (one-fifth of the earth’s land surface), causing a warming, expansion, and acidification of earth’s oceans, leading to a dangerous rise in sea level.
The warming is already wreaking of havoc on earth’s biological systems, including humans, most notably in poorer, tropical countries, many of which are already experiencing grave losses due to extreme weather events, such as drought, heat waves and severe storms, along with unprecedented flooding, all of which had been scientifically predicted well over a century ago!
The warming has been compounded by the increasing loss of vegetation, particularly the loss of the tropical rainforests, which had been naturally sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, but not anymore, by the ones which have been replaced by other forms of development or money producing mono-culture agriculture.
Global warming from human causes is not rocket science, despite what the flat earth believers may still be claiming. However, saying that human-caused global warming is not occurring, because it has not been “proven” to be happening – as of this February 29, 2016, is utterly preposterous, and those who claim human-caused global warming is not happening are either fools or worse yet – liars.
World Bank Concludes Global Warming Will Hurt Poor Countries the Most

World Bank Group President Jim Yong Kim
More than 100 million people could be pushed back into poverty within 15 years due to rising temperatures and extreme weather, the World Bank has warned.
In a new report released Sunday, November 22, 2015, the World Bank said climate change was already preventing people escaping poverty but the situation could get much worse.
“This report sends a clear message that ending poverty will not be possible unless we take strong action to reduce the threat of climate change on poor people and dramatically reduce harmful emissions,” said World Bank Group President Jim Yong Kim.
Crop failures due to drought, big rises in food prices after “extreme weather events,” and a higher incidence of disease following heat waves and floods would hurt the poorest the hardest, the World Bank said in a statement.
The report found people in Africa and South Asia were especially vulnerable.
Stephane Hallegate, an economist who led the team preparing report, said that the future for these 100 million people was not set in stone.
“We have a window of opportunity to achieve our poverty objectives in the face of climate change, provided we make wise policy choices now,” he said.
That would mean tackling the cause of climate change by reducing greenhouse gas emissions, as well as taking steps to reduce the impact on the poor such as improved social safety nets and healthcare, building better flood defenses and developing climate-resistant crops, the report said.
The report comes roughly a month before top officials from around the world will attend the U.N. Climate Change Conference in Paris.
Previously, Nature Climate Change published studies indicating climate change could make parts of the Middle East too hot for human beings to survive.
Catastrophic Climate Change and National Security

World faces catastrophic climate change unless it takes action, National Security Adviser Susan Rice tells Stanford University audience 12 October 2015
Selected Remarks by National Security Adviser Susan E. Rice on Climate Change and National Security at Stanford University, October 12, 2015: [Full Text of Speech]
… In 1985—fall quarter of my senior year—scientists from around the world met to express concern that a buildup of greenhouse gasses, and specifically carbon dioxide, would result in “a rise of global mean temperature…greater than any in man’s history.” By 1990, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change issued its first report, detailing how a warming climate would affect our ecosystem. There have since been four more reports, each with more sophisticated science to support ever more dire warnings.
So, it’s not that we didn’t see climate change coming. It’s that for the better part of three decades we failed, repeatedly, to treat this challenge with the seriousness and the urgency it deserves. As an international community, we succumbed to divisive global politics that set developing countries against industrialized nations and stymied international consensus on climate change.
At home, we succumbed to divisive domestic politics that allowed entrenched interests to push a calculated agenda of doubt, denial, and delay. And, we focused, quite understandably, on other critical national security priorities—from coming to grips with globalization, halting proliferation, and above all, keeping the American people safe in a post-9/11 world….
We are seizing opportunities and meeting challenges head on. And, today, we face no greater long-term challenge than climate change, an advancing menace that imperils so many of the other things we hope to achieve. That’s why, under President Obama, we have put combating climate change at the very center of our national security agenda….
In the past 15 years, we’ve had 14 of the hottest years on record—which is exactly the kind of change those climate scientists back in 1985 suggested we could be seeing by now. Last year, 2014, was the hottest. And, scientists say there’s a 97 percent chance that we’ll set a new record again this year. The seas have risen about eight inches over the past 100 years, and they’re now rising at roughly double the rate they did in the 20th century. Arctic sea ice is shrinking. Permafrost is thawing. The Antarctic ice shelf is breaking up faster than anticipated. Storms are getting stronger. Extreme precipitation events are becoming more frequent. Heat waves are growing more intense. The bottom line is this: we’re on a collision course with climate impacts that have inescapable implications for our national security. Let me sketch out a few of them.
First, climate change is a direct threat to the prosperity and safety of the American people. We’re losing billions of dollars in failed crops due to extreme drought. Millions of acres of forest have been lost to fire. In addition to longer fire seasons and drier summers here in the West, on the East Coast we’re seeing record rain events. Last week in the Carolinas, unprecedented amounts of rain fell—enough in just five days to put a serious dent in California’s multi-year drought. And, while we can’t say that climate change is the direct cause of any specific weather event, these are exactly the trends that we expect to see more of, if climate trends continue on their current trajectory.
Along our coasts, we’ve got thousands of miles of roads and railways, 100 energy facilities, communities of millions—all of which are vulnerable to sea-level rise. Remember Super Storm Sandy—how it hobbled America’s largest city and plunged everyone south of 34th Street into darkness for days? We saw a cascading failure of infrastructure. Water flooded an electrical substation, and backup power was either flooded or insufficient. Over 6,000 patients had to be evacuated from powerless hospitals down stairwells. Transportation broke down, because you can’t pump gas without electricity. Wastewater treatment plants shut down. One critical sector pulled down other vital systems. And, with warmer oceans and higher seas, New York City will have to be prepared for Sandy-level flooding to happen every 25 years.
When I visited Alaska with President Obama last month, we saw rapidly disappearing glaciers and a native community whose island home is already being washed away. The question for them is not if they will have to abandon their traditional homes and way of life, but when. These are real threats to our homeland security, and they’re happening now.
Second, climate change will impact our national defense. We’ve got military installations that are imperiled by the same rising seas as our civilian infrastructure. Here in the western United States, ranges where our troops train are jeopardized by heat and drought. In fact, this summer we had to cancel some training exercises, because it got too hot.
Climate change means operating in more severe weather conditions, increasing the wear on both service members and their equipment. There will also be new demands on our military. A thawing Arctic means 1,000 miles of Arctic coastline and new sea lanes to secure. Around the world, more intense storms—like the massive typhoon that decimated part of the Philippines two years ago—will mean more frequent humanitarian relief missions. And, our military will have to deal with increased instability and conflict around the world.
That’s a third major national security concern, because climate change is what the Department of Defense calls a “threat multiplier”—which means, even if climate change isn’t the spark that directly ignites conflict, it increases the size of the powder keg. A changing climate makes it harder for farmers to grow crops, fishermen to catch enough fish, herders to tend their livestock—it makes it harder for countries to feed their people. And humans, like every other species on this planet, scatter when their environment can no longer sustain them. As the Earth heats up, many countries will experience growing competition for reduced food and water resources. Rather than stay and starve, people will fight for their survival.
All of these consequences are exacerbated in fragile, developing states that are least equipped to handle strains on their resources. In Nigeria, prolonged drought contributed to the instability and dissatisfaction that Boko Haram exploits. The genocide in Darfur began, in part, as a drought-driven conflict. In the years prior to civil war breaking out in Syria, that country also experienced its worst drought on record. Farming families moved en masse into urban centers, increasing political unrest and further priming the country for conflict. In fact, last year, a Stanford research group determined that a rise in temperature is linked with a statistically significant increase in the frequency of conflict. There is already an unholy nexus between human insecurity, humanitarian crises, and state failure—climate change makes it that much worse.
Around the world, more than 100 million people now live less than one meter above sea level—including entire island countries in the Caribbean, the Pacific and the Indian Oceans. Consider the impacts—to the global economy and to our shared security—when rising seas begin to swallow nations whole.
Fourth, we face spreading diseases and mounting threats to global health. Already, more mosquito-borne diseases are spreading from the tropics to temperate zones as climates warm. Viruses like West Nile and Chikungunya are growing more prevalent in the United States. India is currently in the grip of the worst dengue fever outbreak in years. Livestock diseases are expanding northward into Europe. These advancing diseases cost billions of dollars a year to treat and contain, not to mention the immeasurable cost in human lives and suffering.
Finally, we cannot dismiss the worst-case predictions of catastrophic, irreparable damage to our environment. If the Greenland ice sheet melts, seas could rise not just the one to four feet many scientists predict, but eventually as much as 20 feet. If the oceans continue to acidify, it will devastate the marine coral reefs, compromising the food chain, and imperiling a major source of protein for 3 billion people worldwide.
These aren’t marginal threats. They put at risk the health and safety of people on every continent.
One-year Anniversary of “Planet Earth: It Needs Our Help Now More Than Ever”, Broadcast on WORT-FM’s Public Access Hour on Labor Day 2014

Last year on Labor Day WORT-FM in Madison, Wisconsin I had the privilege of recording an hour of music and commentary on a subject I have researched for going on 16 years now: the likely effects of rising greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere, in the oceans, on the landscape; in other words, our planet earth. Since other than president Obama, Pope Francis, the environmental community and the state of California are about the only ones talking seriously about starting to do something to head off what is certain to be catastrophic effects upon our planet and all its livings things in decades and centuries to come, it only seem appropriate to remind folks who would like to listen to the show again. Here it is. Planet Earth – It Needs Our Help More than Ever!
Touring Alaska last month to shine a spotlight on global warming, President Obama warned that “climate change is no longer some far-off problem. It is happening here; it is happening now. Climate change is already disrupting our agriculture and ecosystems, our water and food supplies, our energy, our infrastructure, human health, human safety. Now. Today.”
This wasn’t supposed to happen. In 2009, 114 countries signed the Copenhagen Accord, agreeing “to stabilize greenhouse gas concentration in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic interference with the climate system;” “recognizing the scientific view” that the increase in global temperature should be held to no more than 2 degrees Celsius” (3.6 degrees Fahrenheit) above the pre-industrial level; and promising greater “long-term cooperative action to combat climate change.”
Paradoxically, an accord that should have spurred the world to immediate action instead seemed to offer some breathing room. Two degrees was meant to be a ceiling, but repeated references to an internationally agreed-upon “threshold” led many people to believe that nothing really bad could happen below 2 degrees—or worse yet, that the number itself was negotiable. Perhaps the biggest failure of the Copenhagen Accord was its pact for “long-term” action. Forty years ago, climate change was a “long-term” problem. Today it’s an emergency.
As we’re coming ever so close to the dreaded 2-degree mark, which will have devastating effects especially on people and families less economically fortunate, everywhere, Pope Francis last week called upon the members of the U.S. Congress to find solutions to the problems of growing poverty, everywhere, and climate change, including warming and acidification of the oceans. As civilization’s industrial machinery marches on, we’re already at 400 ppm of carbon dioxide, and likely to go much higher and faster under current “business as usual” practices continue.
Such numbers may mean little to the general public, but they matter a lot to negotiators who will be at Paris climate change talks in December. Unfortunately, the numbers that these negotiators plan to propose will only be part of non-legally-binding pledges—and they represent only what is achievable without too much difficulty, rather than the drastic austerity measures needed to stabilize emissions. In fact, 2 degrees is not an upper limit that the nations of the world recognize and respect, only a target that negotiators know they will overshoot with their expected pledges. The very idea that the Paris conference is a negotiation is ridiculous. You can’t negotiate with the atmosphere.
What were they thinking? As Naomi Klein points out in her book This Changes Everything, the 2 degree goal “has always been a highly political choice that has more to do with minimizing economic disruption than with protecting the greatest number of people.” In theory, the Copenhagen Accord relied on the best available science of the time—an international scientific symposium held in 2005 and assessment reports published by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) in 2007 and earlier, which in turn were based on even older scientific studies. You can trace the 2 degrees notion all the way back to a 1977 paper by Yale economist William D. Nordhaus.
In hindsight, though, the idea that even 2 degrees of warming would be tolerable is baffling. Homo sapiens have never lived in a world that hot. In an excellent series of special reports for CNN on what 2 degrees of global warming would mean, John D. Sutter lists some of the expected impacts: a melting Arctic, enormous wildfires, more intense hurricanes, water shortages, reduced crop yields, and animals and plants at risk of extinction. Even if warming can be held to 2 degrees, scientists predict that global sea level will rise by at least 20 feet as a result.
The Climate Vulnerable Forum, a coalition of 20 nations that expect severe global-warming effects, has called the 2-degree goal “inadequate” to protect fundamental human rights. “How can we possibly subscribe to more than double the current warming?” asked Mary Ann Lucille L. Sering, secretary of the Philippines Climate Change Commission.
Although the 2-degree target was endorsed in Copenhagen in 2009, and again in Cancún the following year, the parties also agreed to periodically review the adequacy of the target and to consider strengthening it. The majority of countries that have signed and ratified the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change now support a lower target of 1.5 degrees, and a review process reported that the lower limit would be “preferable” but that the science supporting it is “less robust.”
What is feasible? The World Bank has warned that a 1.5-degree rise is “locked in,” and that we’re headed toward a warming of 4 degrees by the end of the century. “Scientists, policy-makers and the public already accept that progress will not be enough to keep global average temperature rise within the 2°C limit,” wrote Oliver Geden, head of the EU Research Division at the German Institute for International and Security Affairs, in a recent Nature commentary. “The negotiations’ goal has become what is politically possible, not what is environmentally desirable.”
If you add up the pledges that have been made so far, and nations keep their promises, the world is in for about 3 degrees of warming by 2100. Limiting the warming to 2 degrees would require rapid emissions reductions over the next few decades, declining to zero net emissions shortly after 2050.
It is still possible to limit global warming to 1.5 degrees by 2100 (after a temporary overshoot), according to a paper published in Nature Climate Change a few months ago. But it would mean becoming carbon neutral even earlier than required for a 2-degree scenario.
A national security approach. President Obama made headlines in Alaska—and before that, New Orleans—with fervent talk about the urgency of the climate problem, the need to make communities more resilient, and the “failure of government to look out for its own citizens.” Can this be the same president who, a few months earlier, gave Royal Dutch Shell permission to begin drilling for oil off the coast of Alaska? Developing fossil fuel resources in the Arctic is “incommensurate with efforts to limit average global warming to 2°C,” according to a study by scientists at University College London.
There is an alternative to meaningless numbers and endless negotiations: going to war against climate change. If the United States can spend nearly $1.7 trillion on the “war on terror,”surely we can spend at least that much to keep our planet from overheating.
The 2-degree goal was chosen based on what was considered to be a scientific consensus about the most likely scenario for climate change. That is not how national security risks are evaluated. “When we think about keeping our country safe, we always consider the worst case scenarios,” said British Foreign Office Minister Baroness Joyce Anelay in a statement introducing a new climate risk assessment commissioned by her office. “That is what guides our policies on nuclear non-proliferation, counter-terrorism, and conflict prevention. We have to think about climate change the same way.”
In a foreword to the report, Anelay writes: “We must remember that in one way, climate change differs from any other subject of diplomatic negotiation: It is governed by a physical process. A process where the risk increases over time, and will continue to do so until we have entirely dealt with its cause.”
Increased risk is not an abstraction. It is record-setting heat, year after year. It is coastal erosion washing away villages in Alaska. It is massive wildfires raging in the American West. “We have to attack these at the source, which is carbon pollution,” Washington Gov. Jay Inslee told the Northwest News Network after flying over the worst fires in his state’s history. “It is difficult to comprehend a central fact of these fires,” Inslee said, “which is nature bats last.” Unfortunately, there won’t be any extra innings.
By Dawn Stover, from Bulleten of Atomic Scientists
Stover is a science writer based in the Pacific Northwest and is a contributing editor at the Bulletin. Her work has appeared in Scientific American, Conservation, Popular Science, New Scientist, The New York Times, and other publications. One of her articles is included in the 2010 Best American Science and Nature Writing, and another article was awarded a special citation by the Knight-Risser Prize for Western Environmental Journalism.
NASA: Sea Level Rise of Several Feet is UNAVOIDABLE!

[Tide gauges have been used to measure sea level for more than 130 years. Satellite measurements now complement the historical record. (NASA Earth Observatory image by Joshua Stevens, based on data from the Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organization and NOAA)]
For thousands of years, sea level has remained relatively stable and human communities have settled along the planet’s coastlines. But now Earth’s seas are rising. Globally, sea level has risen about eight inches since the beginning of the 20th century and more than two inches in the last 20 years alone. According to the federal National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), “all signs suggest that this rise is accelerating”.
Seas around the world have risen an average of nearly 3 inches since 1992, with some locations rising more than 9 inches due to natural variation, according to the latest satellite measurements from NASA and its partners. An intensive research effort now underway, aided by NASA observations and analysis, points to “an unavoidable rise of several feet in the future”.
“Sea level rise is a natural [physical] consequence of the warming of our planet”, states NASA’s press release dated August 26, 2015. “We know this from basic physics. When water heats up, it expands. So when the ocean warms, sea level rises. When ice is exposed to heat, it melts. And when ice on land melts and water runs into the ocean [water from unprecedented ice and snow melt off Antarctica, Greenland, land areas north of permafrost region in Northern Hemisphere, mountainous glaciers receding, worldwide] sea level rises”.
As the ocean has warmed, polar ice has melted, and porous landmasses have subsided, global mean sea level has risen by 8 inches (20 centimeters) since 1870. The rate of sea level rise is faster now than at any time in the past 2,000 years, and that rate has doubled in the past two decades.
While NASA and other agencies continue to monitor the warming of the ocean and changes to the planet’s land masses, the biggest concern is what will happen to the ancient ice sheets covering Greenland and Antarctica, which continue to send out alerts that a warming planet is affecting their stability.
NASA has been recording the height of the ocean surface from space since 1992, recording about 2.9 inches (7.4 centimeters) of sea level rise averaged for all the oceans in that 23 year period.
In 2002, NASA and the German space agency launched the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) twin satellites, capable of measuring the movement of mass, hence gravity, around Earth at intervals of every 30 days. GRACE has found that earth’s land masses move very little in a month; however, earth’s water masses move through melting, evaporation, precipitation and other processes. GRACE records these movements of water around the planet, while a new NASA network of more than 3,000 floating ocean sensors spread across the entire open ocean supplement that ocean water level data.
Observations from the new NASA ocean level data collection systems have revolutionized scientists’ understanding of contemporary sea level rise and its causes. NASA’s newest release state that: “We know that today’s sea level rise is about one-third the result of the warming of existing ocean water, with the remainder coming from melting land ice”, adding that “currently, regional differences in sea level rise are dominated by the effects of ocean currents and well known cycles, such as the Pacific Ocean’s El Niño phenomenon and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation.” But as the ice sheets located closer to the poles of the planet (which receive less direct solar radiation due to the tilting of the planet as it orbits the Sun), and the once “permanent” ice located at higher elevations around the world continues to melt as a direct result of measurably warming temperatures occurring as a direct consequence of a stronger greenhouse effect that is already unnaturally high due to human activities such as fossil fuel burning, deforestation, and paving over the earth’s still green landscape. NASA scientists now predict that the increasing meltwater resulting from the stronger greenhouse effect will overtake the formerly natural causes of regional variations of the ocean water levels and be the most significant contributor to the overall rise in sea level.
The recent advances in observing the world’s frozen regions using satellite measurements from NASA and its participating organizations have allowed scientists to accurately estimate annual ice losses from Greenland and Antarctica. Not only can they now determine how much sea level around the world is changing – as measured by satellite for the past 23 years – but they can also determine how much of the sea level rise is being caused by our warming of the earth’s biosphere, which includes both the atmosphere at or near the surface, the oceans, the land surface, and the biota (plant and animal kingdoms) that all together comprise earth’s biosphere.
GRACE’s record, spanning over the last decade, shows that the ice loss around the planet is now accelerating in Greenland and West Antarctica. The record shows Greenland has shed on average 303 gigatons of ice every year since 2004, while Antarctica has lost on average 118 gigatons of ice per year. Much of Antarctica’s ice loss has been shown to come from West Antarctica’s ice loss. Greenland’s ice loss has accelerated by 31 gigatons of ice per year, every year since 2004, while West Antarctica’s ice loss has accelerated to 28 gigatons per year.
“Given what we know now about how the ocean expands as it warms and how ice sheets and glaciers are adding water to the seas, it’s pretty certain we are locked into at least 3 feet of sea level rise and probably more,” said Steve Nerem of the University of Colorado, Boulder, and lead of NASA’s new Sea Level Change Team.
The Greenland Ice Sheet, spanning 660,000 square miles (an area almost as big as Alaska), and with a thickness at its highest point of almost 2 miles, has the potential to raise the world’s oceans by more than 20 feet. Situated in the Arctic, which is warming at twice the rate of the rest of the planet, Greenland has been shedding more ice in the summer than it gains back in the winter since 1992.
“In Greenland, everything got warmer at the same time: the air, the ocean surface, the depths of the ocean,” said Ian Joughin, a glaciologist at University of Washington. “We don’t really understand which part of that warming is having the biggest effect on the glaciers.”
What scientists do know is that warming Arctic temperatures – and a darkening surface of the Greenland ice sheet – are causing so much summer melting that it is now the dominant factor in Greenland’s contribution to sea level rise.
NASA has found that Greenland’s summer melt season now lasts 70 days longer than it did in the early 1970s. Every summer, warmer air temperatures cause melt over about half of the surface of the ice sheet – although recently, 2012 saw an extreme event where 97 percent of the ice sheet experienced melt at its top layer.
Greenland’s massive glaciers have sped up, too. Though many of the glaciers in the southeast, west and northwest of the island – an area that experienced quick thinning from 2000 to 2006 – have now slowed down, the melting rate at other areas Greenland’s massive ice sheet has not slowed. A study last year showed that the northeast Greenland ice stream had increased its ice loss rate due to warmer air temperatures.
“The early 2000s was when some big things revealed themselves, such as when we saw the fastest glacier we knew of, the Jakobshavn ice stream in Greenland, double its speed,” said Waleed Abdalati, director of the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences, Boulder, Colorado, and former NASA chief scientist. “The subsequent surprise was that these changes could be sustained for a decade – Jakobshavn is still going fast”, Abdalati said.
The Antarctic Ice Sheet covers nearly 5.4 million square miles, and area larger than the United States and India combined, and contains enough ice to raise the ocean level by about 190 feet. The Transantarctic Mountains split Antarctica in two major regions: West Antarctica and the much larger East Antarctica.
Though Antarctica’s contribution to sea level rise is still at less than 0.02 inches (0.5 millimeters) per year, several events over the past decade and a half have prompted experts to start warning about the possibility of more rapid changes this century.
The mountainous horn of the continent, the Antarctic Peninsula, gave one of the earliest warnings on the impact of a changing climate in Antarctica when warm air and warmer ocean temperatures led to the dramatically fast breakup of the Larsen B ice shelf in 2002. In about a month, 1,250 square miles of floating ice that had been stable for over 10,000 years were gone. In the following years, other ice shelves in the Peninsula, including the last remainder of Larsen B, collapsed, speeding up in the flow of the land lying glaciers that they were buttressing against the warming ocean.
In 2014, two studies focusing on the acceleration of the glaciers in the Amundsen Sea sector of West Antarctica showed that its collapse is currently well underway. And while one of the studies speculated that the demise of the ice overlaying West Antarctica could take as long as 200 to 1,000 years, depending on how rapidly the ocean heats up, both studies concurred that its collapse is already unstoppable, and that when it does collapse, the melt water will add up to 12 feet of sea level rise to the oceans.
The wind is also a factor in determining the timing of West Antarctica’s collapse. The “westerlies”, the winds that spin the ocean waters around Antarctica, are known to have intensified during the last decade, pushing the cold top layer away from the land, and thus allowing the warmer, deeper waters to rise and spill over the border of the continental shelf, flowing all the way back to the base of many of the ice shelves jetting out from the continent. As the ice shelves weaken from underneath, the glaciers behind them are predicted to speed up.
East Antarctica’s massive ice sheet, as vast as the lower continental U.S., remains an unknown in projections of sea level rise. Though it appears to be stable, a recent study on Totten Glacier, East Antarctica’s largest and most rapidly thinning glacier, hints otherwise. Research found two deep troughs that could lead warm ocean water to the base of the glacier and melt it in a similar way to what’s happening to the glaciers in West Antarctica. Other sectors grounded below sea level, such as the Cook Ice Shelf, Ninnis, Mertz and Frost glaciers, have also been found to be losing mass.
For the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which largely rests on a bed that lies below sea level, the main driver of ice loss is the ocean. The waters of the Southern Ocean are layered: on top and at the bottom, the temperatures are frigid, but the middle layer is warm. The westerlies, the winds that spin the ocean waters around Antarctica, have intensified during the last decade, pushing the cold top layer away from the land. This allows the warmer, deeper waters to rise and spill over the border of the continental shelf, flowing all the way back to the base of many ice shelves. As the ice shelves weaken from underneath, the glaciers behind them speed up.
East Antarctica’s massive ice sheet, as vast as the lower continental U.S., remains the main unknown in projections of sea level rise. Though it appears to be stable, a recent study on Totten Glacier, East Antarctica’s largest and most rapidly thinning glacier, hints otherwise. The research found two deep troughs that could lead warm ocean water to the base of the glacier and melt it in a similar way to what’s happening to the glaciers in West Antarctica. Other sectors grounded below sea level, such as the Cook Ice Shelf, Ninnis, Mertz and Frost glaciers, are also losing mass.
CAFO’s Pollution of Kewaunee County Groundwater
A coalition of local, state and national organizations led by the Socially Responsible Agricultural Project (SRAP) released a damaging report and recommendations for reform on the hazardous, uncontrolled growth of industrial dairy pollution and its impact on the residents of Kewaunee County, Wisconsin. “The RAP SHEETS: Industrial Dairies in Kewaunee County, Wisconsin” is the result of more than a year-long investigation of government documents identifying negligent management of industrial dairy concentrated animal feeding operations (CAFOs) and a lack of oversight and enforcement by the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources (WDNR) as catalysts for skyrocketing pollution that has pushed Kewaunee County to an environmental and public health crisis. The facilities in this report collectively received $14,417,910 of taxpayer-funded subsidies between the years 1995 – 2013.
Partner organizations Family Farm Defenders and Kewaunee CARES joined SRAP to research, publish and provide recommendations for the first-of-its-kind report on the multiple violations, hundreds of manure management failures and a host of operational problems at the 16 large CAFOs operating within Kewaunee County. Reform proposals include reversing the industry-friendly 2004 Livestock Facility Siting Law and reinstating community control over CAFO zoning and construction — an action that would begin to restore Kewaunee County, and save other Wisconsin counties from a similar fate.




Recent Comments