26. A Reflection on the National Governor’s Association Meeting in Milwaukee this Month
Yosemite National Park – August 24, 2013. “”No temple made with hands can compare with Yosemite… The grandest of all special temples of Nature . (John Muir)
I was disappointed reading the Milwaukee Journal/Sentinel’s report on the National Governors Association’s meeting held earlier this month in Milwaukee, particularly that their agenda did not even include the growing threat of climate change and what steps the governors might take to reduce their state’s contributions to the rising concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, as well as how they might better help their state populations cope with increasingly more severe weather conditions already being witnessed worldwide. The wildfire that has spread into Yosemite National Park is now being called “one of the largest wildfires in recent California history”. It is said to have already burned more than 125,000 acres.
25. Most Prestigious Worldwide Science Organization and NBC Sound Alarm on Global Warming

NBC Nightly News | August 20, 2013
NBC ‘s Lester Holt is anchoring NBC’s “Nightly News” program this week while regular news anchor Brian William is having reconstructive knee surgery. He reports on a recent draft of the United Nation’s upcoming climate report, which states what scientists have been warning about for several years – that the main cause of long-term global warming is carbon dioxide emissions.
“Tonight a leaked report from one of the world’s most prestigious group of scientists, winners of the Nobel prize , has a lot of people taking notice because of the alarming conclusions about climate change . NBC’s Ann Curry recently traveled to one of the most breathtaking places on earth where folks are seeing their way of life disappear before their eyes. She joins us now in the studio. Ann, nice to see you.”
For several years Greenland’s native Inuits have witnessed the effects of climate change near the North Pole. The key finding in this leaked draft report is that it’s extremely likely, as in greater than 95%, that human activity is the main cause of the planet’s temperature rise in the last 60 years. Well, recently our news team went looking for answers in a place where the ice melt is unprecedented. Reporting from the top of the world in arctic, Greenland, scientists like Dr. Jason Box study the icy landscape. He says all this might be lost to climate change: “There’s no debate, it’s really quite simple. we’ve overloaded the atmosphere with trapping gas, and the rest are just details”, Box said.
NBC : The new report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change seems to confirm what Box and other scientists have been warning long before the draft was leaked. Among the findings: “that the main cause of long-term warming is carbon dioxide emissions , that sea levels could rise about three feet by the end of the century , and that even if we stop producing carbon emissions now, climate change will persist for hundreds of years.”
Here in what’s known as Iceberg Alley, Box, who’s been studying the arctic for 20 years, says “the ice is now melting at a pace never seen before, affecting weather systems” . Reporter: “So in ways that people don’t fully yet realize,climate change is affected us in America and across the world?”
Dr. Box: “Yeah. there are manifold that climate change is having impact. The arctic is a very useful bellwether of change. And it’s ringing.”
Reporter: But in Greenland, once called Eskimo (now called Inuits), they don’t need a scientist to tell them about climate: “the sea ice are disappearing”. The Inuit leader says melting ice means his people struggle to reach their traditional hunting grounds. Some have even fallen through the thinning ice and died. You’re saying that a way of life is so threatened, it could die? It could be lost forever?
Inuit leader: “The only humans around the North Pole in the Arctic are us. We have been here for thousands of years. and we tell you, things are changing. and you will feel it, maybe tomorrow.”
Ann Courry: “His message essentially is that we in the industrialized world are using more than our fair share and that our children and our grandchildren will pay the price, Lester”.
Lester Holt: “Very Sobering, Ann, thank you”.
24. Bill to Raise Speed Limit in Wisconsin to 70 Miles Per Hour Would Add to Already Steep Pace of Global Warming
Just a day after Illinois Governor Pat Quinn signed a bill raising the speed limit on rural highways in his state to 70 mph, Wisconsin Rep. Paul Tittl, R-Manitowoc, on Tuesday called for the same thing in Wisconsin
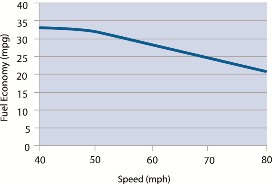
. Such a bill would promote burning more fuel per mile driven in the state, because gas mileage usually rapidly decreases each mile driven faster over 50 miles per hour.
The result of burning more fuel in motor vehicles driven in the state would result in increased amounts greenhouses gases, such as carbon dioxide, from the transportation sector of the state, leading to higher rates of global warming.
Illinois was the 35th state to increase speed limits since Congress allowed it in 1995, doing away with widely ignored federal speed limits of 55 mph on most roads and 65 mph on rural roads. The federal speed limit law was passed to reduce fuel consumption after the 1973 oil embargo.
An international team of scientists has found with near certainty that human activity is the cause of most of the temperature increases of recent decades, and warns that sea levels could rise by more than 3 feet by the end of the century if emissions continue at a runaway pace.
A 3-foot rise would endanger many of the world’s great cities — among them London; Shanghai; Venice; Sydney; Miami; New Orleans; and New York.
The international scientists’ summary of the next big U.N. climate report largely dismisses a recent slowdown in the pace of warming, which is often cited by climate-change contrarians, as probably related to short-term factors. The report emphasizes that the basic facts giving rise to global alarm about future climate change are more established than ever, and it reiterates that the consequences of runaway emissions are likely to be profound.
The Wisconsin bill would have to pass the Senate and Assembly, and be signed by Governor Walker, before taking effect.
Tittl’s proposal has the backing of Republican Assembly Speaker Robin Vos, who has said he wants a vote on the measure in September.
While each vehicle reaches its optimal fuel economy at a different speed (or range of speeds), gas mileage usually decreases rapidly at speeds above 50 mph.
23. Governor Scott Walker Signs “No Climate Tax Pledge”
Wisconsin Governor Scott Walker is among signers of Koch-backed ‘No Climate Tax Pledge’
There’s a new pledge in town, and several Wisconsin conservatives have signed on.
This pledge is called the “No Climate Tax Pledge,” but it might as well be called the “Koch Brothers Protection Pledge,” since it was devised by a group co-founded and backed by the billionaire brothers whose companies, according to the EPA, emitted over 24 million tons of carbon dioxide in 2011.
The pledge was devised by Americans for Prosperity, a tea party group founded by the Koch brothers and Koch Industries board member Richard Fink.
“While the pledge began with a marginal following, an energized turnout of conservative voters in the 2010 election swept 85 freshman Republicans into the House,” the authors of the report write. “Of those 85 Republicans, 76 signed the Koch pledge as candidates. And 57 of those 76 received campaign contributions from Koch Industries’ political action committee.”
Those newly elected Republicans helped push through funding cuts for the Environmental Protection Agency and tried to roll back the agency’s regulatory powers, as well as being obstacles to enactment of laws to address climate change, the report says.
In addition to Walker and Kleefisch, Wisconsin signers of the pledge, all Republicans, are U.S. Sen. Ron Johnson, U.S. Reps. Jim Sensenbrenner, Sean Duffy and Reid Ribble, state Sens. Leah Vukmir, Alberta Darling, Glenn Grothman and Mary Lazich, and state Reps. Dale Kooyenga, Don Pridemore, Jim Ott and Bill Kramer.
In addition to Walker and Kleefisch, Wisconsin signers of the pledge, all Republicans, are U.S. Sen. Ron Johnson, U.S. Reps. Jim Sensenbrenner, Sean Duffy and Reid Ribble, state Sens. Leah Vukmir, Alberta Darling, Glenn Grothman and Mary Lazich, and state Reps. Dale Kooyenga, Don Pridemore, Jim Ott and Bill Kramer.
21. Recent Heat-related Deaths in Wisconsin
Heat-related deaths and sicknesses are likely to become much more commonplace in the U.S. and the rest of world as a consequence of increased global warming, primarily caused by human activities. Following are six deaths that have been reported by the news media in Wisconsin:
Milwaukee authorities are reporting a fourth and fifth suspected heat-related death. The Milwaukee County Medical Examiner’s Office says the latest victims are a 64-year-old woman, who died early Saturday, and a 69-year-old man who died Friday.
They said the woman developed breathing problems in her Milwaukee home, where the air temperature was 93 degrees. Her body temperature was 110 degrees. She had an air conditioner, but was unable to install it on her own. All the windows in her home were closed, and the family never opened them because they feared shots being fired in the neighborhood. They said the man was admitted to St. Joseph’s Hospital from a home in Milwaukee on Thursday with a body temperature of 102 degrees and died Friday night.
The bodies of two of the other dead men, ages 71 and 79, were found in separate houses Friday. In both cases, the medical examiner said the houses were sealed with no fans on and no air conditioning on in the house. The fifth victim is a 44-year-old man who was found unresponsive in an alley Wednesday evening in Milwaukee and pronounced dead in an intensive-care unit Thursday.
Finally, the death of a two-year old boy found by a deputy in the trunk of a car on his parents’ property near Centuria, Wisconsin, has been confirmed to be heat-related. Preliminary autopsy results released Friday said the boy likely died of hyperthermia — a condition in which the body temperature spikes from high and prolonged heat.
The National Weather Service says Milwaukee has recorded four consecutive days of highs in the mid-90s this week, with the “heat index” (factors in humidity) registering more than 100 degrees Fehrenhei.
20. Obama’s Speech on Fighting Global Warming: “Too Little, Too Late”?

The president’s speech was great in tone and in the way he showed we need immediate action to regulate carbon dioxide emissions from power plants and deal with other countries of the world in the collective reduction in worldwide emissions of greenhouse gases. But the plan lacked detail, especially in how we should all be CONSERVING more energy that is generated by fuel burning in everything we do, especially driving less, flying less (or not at all), and using less energy in our homes and in the places where we visit.
The U. S. Energy Information Administration (EIA) estimates that U.S. gasoline and diesel fuel consumption for transportation in 2012 resulted in the emission of about 1,089 million metric tons from gasoline and 422 million metric tons of CO2 from diesal fuel burning to the atmosphere, respectively, for a total of 1,511 million metric tons of atmospheric CO2 in 2012. This total was equivalent to 83% of total CO2 emissions by the U.S. transportation sector and 29% of total U.S. energy-related CO2 emissions.
Regarding air travel, it is often said that transportation by plane usually results in by far the largest quantities of greenhouse gases (GHG’s) emitted by a person in a year. GHG’s emitted (CO2 and nitrous oxide). This is due to the tremendous quantities of fossil fuels burned in takeoff, climbing and cruising at high elevation in a heavy jet airliner.
In 2011, the average annual electricity consumption for a U.S. residential utility customer was 11,280 kWh. Louisiana had the highest annual consumption at 16,176 kWh and Maine the lowest at 6,252 kWh.
To meaningfully reduce our emissions from transportation and household/business use our Congressional representatives and senators needs to ENACT MAJOR PROGRAMS THIS LEGISLATIVE SESSION. The U. S. Congress should enact programs that offer voluntarily “positive financial incentives” ($) to Americans who limit their carbon dioxide emissions to minimal levels, as measured by their annual mileage driven in automobiles (all registered vehicles they own) over a year’s time. It is not enough to rely on vehicle energy efficiency improvements to reduce CO2 emissions by transportation since studies have shown than most people who buy more fuel efficient cars eventually drive even more miles per year than they did before, not less, which therefore negates the fuel efficiency caused greenhouse gas (GHG) reductions.
These programs should be funded by taking away the many tax exemptions now given to fossil fuel development corporation, reductions in funding the military industrial complex, and by eliminating major expansions to highways and airports and by avoiding the construction of new power sources due to increased conservation of energy in homes and increased energy supplies from wind and solar sources. The money should then be directed into funding for offering positive financial incentives for people to drive less (miles) (or not drive at all); to avoid flying; and to use less fossil fuel derived energy in their homes or businesses. People who already chose to walk, ride buses, and not fly airplanes would benefit financially by this program, as would individuals, families and business who use less fossil fuel derived energy in heating and electrifying their homes and businesses.
More details on the financial incentives plan are contained in: “Positive Financial Incentives: An Environmentally Just Approach for Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions”, published earlier on this blog site on May 9, 2013.
“Our lives begin to end the day we become silent about things that matter.”
— Martin Luther King Jr.
18. President Obama’s Speech on Global Warming – A “Must Read” for Every American
Transcript of President Barack Obama’s June 25, 2013 speech at Georgetown University, Washington, DC, unveiling his new policies to confront global warming:
THE PRESIDENT: Thank you! (Applause.) Thank you, Georgetown! Thank you so much. Everybody, please be seated. And my first announcement today is that you should all take off your jackets. (Laughter.) I’m going to do the same. (Applause.) It’s not that sexy, now. (Laughter.)
It is good to be back on campus, and it is a great privilege to speak from the steps of this historic hall that welcomed Presidents going back to George Washington.
I want to thank your president, President DeGioia, who’s here today. (Applause.) I want to thank him for hosting us. I want to thank the many members of my Cabinet and my administration. I want to thank Leader Pelosi and the members of Congress who are here. We are very grateful for their support.
And I want to say thank you to the Hoyas in the house for having me back. (Applause.) It was important for me to speak directly to your generation, because the decisions that we make now and in the years ahead will have a profound impact on the world that all of you inherit.
On Christmas Eve, 1968, the astronauts of Apollo 8 did a live broadcast from lunar orbit. So Frank Borman, Jim Lovell, William Anders — the first humans to orbit the moon — described what they saw, and they read Scripture from the Book of Genesis to the rest of us back here. And later that night, they took a photo that would change the way we see and think about our world.
It was an image of Earth — beautiful; breathtaking; a glowing marble of blue oceans, and green forests, and brown mountains brushed with white clouds, rising over the surface of the moon.
And while the sight of our planet from space might seem routine today, imagine what it looked like to those of us seeing our home, our planet, for the first time. Imagine what it looked like to children like me. Even the astronauts were amazed. “It makes you realize,” Lovell would say, “just what you have back there on Earth.”
And around the same time we began exploring space, scientists were studying changes taking place in the Earth’s atmosphere. Now, scientists had known since the 1800s that greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide trap heat, and that burning fossil fuels release those gases into the air. That wasn’t news. But in the late 1950s, the National Weather Service began measuring the levels of carbon dioxide in our atmosphere, with the worry that rising levels might someday disrupt the fragile balance that makes our planet so hospitable. And what they’ve found, year after year, is that the levels of carbon pollution in our atmosphere have increased dramatically.
That science, accumulated and reviewed over decades, tells us that our planet is changing in ways that will have profound impacts on all of humankind.
The 12 warmest years in recorded history have all come in the last 15 years. Last year, temperatures in some areas of the ocean reached record highs, and ice in the Arctic shrank to its smallest size on record — faster than most models had predicted it would. These are facts.
Now, we know that no single weather event is caused solely by climate change. Droughts and fires and floods, they go back to ancient times. But we also know that in a world that’s warmer than it used to be, all weather events are affected by a warming planet. The fact that sea level in New York, in New York Harbor, are now a foot higher than a century ago — that didn’t cause Hurricane Sandy, but it certainly contributed to the destruction that left large parts of our mightiest city dark and underwater.
The potential impacts go beyond rising sea levels. Here at home, 2012 was the warmest year in our history. Midwest farms were parched by the worst drought since the Dust Bowl, and then drenched by the wettest spring on record. Western wildfires scorched an area larger than the state of Maryland. Just last week, a heat wave in Alaska shot temperatures into the 90s.
And we know that the costs of these events can be measured in lost lives and lost livelihoods, lost homes, lost businesses, hundreds of billions of dollars in emergency services and disaster relief. In fact, those who are already feeling the effects of climate change don’t have time to deny it — they’re busy dealing with it. Firefighters are braving longer wildfire seasons, and states and federal governments have to figure out how to budget for that. I had to sit on a meeting with the Department of Interior and Agriculture and some of the rest of my team just to figure out how we’re going to pay for more and more expensive fire seasons.
Farmers see crops wilted one year, washed away the next; and the higher food prices get passed on to you, the American consumer. Mountain communities worry about what smaller snowpacks will mean for tourism — and then, families at the bottom of the mountains wonder what it will mean for their drinking water. Americans across the country are already paying the price of inaction in insurance premiums, state and local taxes, and the costs of rebuilding and disaster relief.
So the question is not whether we need to act. The overwhelming judgment of science — of chemistry and physics and millions of measurements — has put all that to rest. Ninety-seven percent of scientists, including, by the way, some who originally disputed the data, have now put that to rest. They’ve acknowledged the planet is warming and human activity is contributing to it.
So the question now is whether we will have the courage to act before it’s too late. And how we answer will have a profound impact on the world that we leave behind not just to you, but to your children and to your grandchildren.
As a President, as a father, and as an American, I’m here to say we need to act.
I refuse to condemn your generation and future generations to a planet that’s beyond fixing. And that’s why, today, I’m announcing a new national climate action plan, and I’m here to enlist your generation’s help in keeping the United States of America a leader — a global leader — in the fight against climate change.
This plan builds on progress that we’ve already made. Last year, I took office — the year that I took office, my administration pledged to reduce America’s greenhouse gas emissions by about 17 percent from their 2005 levels by the end of this decade. And we rolled up our sleeves and we got to work. We doubled the electricity we generated from wind and the sun. We doubled the mileage our cars will get on a gallon of gas by the middle of the next decade.
Here at Georgetown, I unveiled my strategy for a secure energy future. And thanks to the ingenuity of our businesses, we’re starting to produce much more of our own energy. We’re building the first nuclear power plants in more than three decades — in Georgia and South Carolina. For the first time in 18 years, America is poised to produce more of our own oil than we buy from other nations. And today, we produce more natural gas than anybody else. So we’re producing energy. And these advances have grown our economy, they’ve created new jobs, they can’t be shipped overseas — and, by the way, they’ve also helped drive our carbon pollution to its lowest levels in nearly 20 years. Since 2006, no country on Earth has reduced its total carbon pollution by as much as the United States of America.
So it’s a good start. But the reason we’re all here in the heat today is because we know we’ve got more to do.
In my State of the Union address, I urged Congress to come up with a bipartisan, market-based solution to climate change, like the one that Republican and Democratic senators worked on together a few years ago. And I still want to see that happen. I’m willing to work with anyone to make that happen.
But this is a challenge that does not pause for partisan gridlock. It demands our attention now. And this is my plan to meet it — a plan to cut carbon pollution; a plan to protect our country from the impacts of climate change; and a plan to lead the world in a coordinated assault on a changing climate.
This plan begins with cutting carbon pollution by changing the way we use energy — using less dirty energy, using more clean energy, wasting less energy throughout our economy.
Forty-three years ago, Congress passed a law called the Clean Air Act of 1970. It was a good law. The reasoning behind it was simple: New technology can protect our health by protecting the air we breathe from harmful pollution. And that law passed the Senate unanimously. Think about that — it passed the Senate unanimously. It passed the House of Representatives 375 to 1. I don’t know who the one guy was — I haven’t looked that up. You can barely get that many votes to name a post office these days.
It was signed into law by a Republican President. It was later strengthened by another Republican President. This used to be a bipartisan issue.
Six years ago, the Supreme Court ruled that greenhouse gases are pollutants covered by that same Clean Air Act. And they required the Environmental Protection Agency, the EPA, to determine whether they’re a threat to our health and welfare. In 2009, the EPA determined that they are a threat to both our health and our welfare in many different ways — from dirtier air to more common heat waves — and, therefore, subject to regulation.
Today, about 40 percent of America’s carbon pollution comes from our power plants. But here’s the thing: Right now, there are no federal limits to the amount of carbon pollution that those plants can pump into our air. None. Zero. We limit the amount of toxic chemicals like mercury and sulfur and arsenic in our air or our water, but power plants can still dump unlimited amounts of carbon pollution into the air for free. That’s not right, that’s not safe, and it needs to stop.
So today, for the sake of our children, and the health and safety of all Americans, I’m directing the Environmental Protection Agency to put an end to the limitless dumping of carbon pollution from our power plants, and complete new pollution standards for both new and existing power plants.
I’m also directing the EPA to develop these standards in an open and transparent way, to provide flexibility to different states with different needs, and build on the leadership that many states, and cities, and companies have already shown. In fact, many power companies have already begun modernizing their plants, and creating new jobs in the process. Others have shifted to burning cleaner natural gas instead of dirtier fuel sources.
Nearly a dozen states have already implemented or are implementing their own market-based programs to reduce carbon pollution. More than 25 have set energy efficiency targets. More than 35 have set renewable energy targets. Over 1,000 mayors have signed agreements to cut carbon pollution. So the idea of setting higher pollution standards for our power plants is not new. It’s just time for Washington to catch up with the rest of the country. And that’s what we intend to do.
Now, what you’ll hear from the special interests and their allies in Congress is that this will kill jobs and crush the economy, and basically end American free enterprise as we know it. And the reason I know you’ll hear those things is because that’s what they said every time America sets clear rules and better standards for our air and our water and our children’s health. And every time, they’ve been wrong.
For example, in 1970, when we decided through the Clean Air Act to do something about the smog that was choking our cities — and, by the way, most young people here aren’t old enough to remember what it was like, but when I was going to school in 1979-1980 in Los Angeles, there were days where folks couldn’t go outside. And the sunsets were spectacular because of all the pollution in the air.
But at the time when we passed the Clean Air Act to try to get rid of some of this smog, some of the same doomsayers were saying new pollution standards will decimate the auto industry.
Guess what — it didn’t happen. Our air got cleaner.
In 1990, when we decided to do something about acid rain, they said our electricity bills would go up, the lights would go off, businesses around the country would suffer — I quote — “a quiet death.” None of it happened, except we cut acid rain dramatically.
See, the problem with all these tired excuses for inaction is that it suggests a fundamental lack of faith in American business and American ingenuity. These critics seem to think that when we ask our businesses to innovate and reduce pollution and lead, they can’t or they won’t do it. They’ll just kind of give up and quit. But in America, we know that’s not true. Look at our history.
When we restricted cancer-causing chemicals in plastics and leaded fuel in our cars, it didn’t end the plastics industry or the oil industry. American chemists came up with better substitutes. When we phased out CFCs — the gases that were depleting the ozone layer — it didn’t kill off refrigerators or air-conditioners or deodorant. American workers and businesses figured out how to do it better without harming the environment as much.
The fuel standards that we put in place just a few years ago didn’t cripple automakers. The American auto industry retooled, and today, our automakers are selling the best cars in the world at a faster rate than they have in five years — with more hybrid, more plug-in, more fuel-efficient cars for everybody to choose from.
So the point is, if you look at our history, don’t bet against American industry. Don’t bet against American workers. Don’t tell folks that we have to choose between the health of our children or the health of our economy.
The old rules may say we can’t protect our environment and promote economic growth at the same time, but in America, we’ve always used new technologies — we’ve used science; we’ve used research and development and discovery to make the old rules obsolete.
Today, we use more clean energy — more renewables and natural gas — which is supporting hundreds of thousands of good jobs. We waste less energy, which saves you money at the pump and in your pocketbooks. And guess what — our economy is 60 percent bigger than it was 20 years ago, while our carbon emissions are roughly back to where they were 20 years ago.
So, obviously, we can figure this out. It’s not an either/or; it’s a both/and. We’ve got to look after our children; we have to look after our future; and we have to grow the economy and create jobs. We can do all of that as long as we don’t fear the future; instead we seize it.
And, by the way, don’t take my word for it — recently, more than 500 businesses, including giants like GM and Nike, issued a Climate Declaration, calling action on climate change “one of the great economic opportunities of the 21st century.” Walmart is working to cut its carbon pollution by 20 percent and transition completely to renewable energy. Walmart deserves a cheer for that. But think about it. Would the biggest company, the biggest retailer in America — would they really do that if it weren’t good for business, if it weren’t good for their shareholders?
A low-carbon, clean energy economy can be an engine of growth for decades to come. And I want America to build that engine. I want America to build that future — right here in the United States of America. That’s our task.
Now, one thing I want to make sure everybody understands — this does not mean that we’re going to suddenly stop producing fossil fuels. Our economy wouldn’t run very well if it did. And transitioning to a clean energy economy takes time. But when the doomsayers trot out the old warnings that these ambitions will somehow hurt our energy supply, just remind them that America produced more oil than we have in 15 years. What is true is that we can’t just drill our way out of the energy and climate challenge that we face. That’s not possible.
I put forward in the past an all-of-the-above energy strategy, but our energy strategy must be about more than just producing more oil. And, by the way, it’s certainly got to be about more than just building one pipeline.
Now, I know there’s been, for example, a lot of controversy surrounding the proposal to build a pipeline, the Keystone pipeline, that would carry oil from Canadian tar sands down to refineries in the Gulf. And the State Department is going through the final stages of evaluating the proposal. That’s how it’s always been done. But I do want to be clear: Allowing the Keystone pipeline to be built requires a finding that doing so would be in our nation’s interest. And our national interest will be served only if this project does not significantly exacerbate the problem of carbon pollution. The net effects of the pipeline’s impact on our climate will be absolutely critical to determining whether this project is allowed to go forward. It’s relevant.
Now, even as we’re producing more domestic oil, we’re also producing more cleaner-burning natural gas than any other country on Earth. And, again, sometimes there are disputes about natural gas, but let me say this: We should strengthen our position as the top natural gas producer because, in the medium term at least, it not only can provide safe, cheap power, but it can also help reduce our carbon emissions.
Federally supported technology has helped our businesses drill more effectively and extract more gas. And now, we’ll keep working with the industry to make drilling safer and cleaner, to make sure that we’re not seeing methane emissions, and to put people to work modernizing our natural gas infrastructure so that we can power more homes and businesses with cleaner energy.
The bottom line is natural gas is creating jobs. It’s lowering many families’ heat and power bills. And it’s the transition fuel that can power our economy with less carbon pollution even as our businesses work to develop and then deploy more of the technology required for the even cleaner energy economy of the future.
And that brings me to the second way that we’re going to reduce carbon pollution — by using more clean energy. Over the past four years, we’ve doubled the electricity that we generate from zero-carbon wind and solar power. And that means jobs — jobs manufacturing the wind turbines that now generate enough electricity to power nearly 15 million homes; jobs installing the solar panels that now generate more than four times the power at less cost than just a few years ago.
I know some Republicans in Washington dismiss these jobs, but those who do need to call home — because 75 percent of all wind energy in this country is generated in Republican districts. And that may explain why last year, Republican governors in Kansas and Oklahoma and Iowa — Iowa, by the way, a state that harnesses almost 25 percent of its electricity from the wind — helped us in the fight to extend tax credits for wind energy manufacturers and producers. Tens of thousands good jobs were on the line, and those jobs were worth the fight.
And countries like China and Germany are going all in in the race for clean energy. I believe Americans build things better than anybody else. I want America to win that race, but we can’t win it if we’re not in it.
So the plan I’m announcing today will help us double again our energy from wind and sun. Today, I’m directing the Interior Department to green light enough private, renewable energy capacity on public lands to power more than 6 million homes by 2020.
The Department of Defense — the biggest energy consumer in America — will install 3 gigawatts of renewable power on its bases, generating about the same amount of electricity each year as you’d get from burning 3 million tons of coal.
And because billions of your tax dollars continue to still subsidize some of the most profitable corporations in the history of the world, my budget once again calls for Congress to end the tax breaks for big oil companies, and invest in the clean-energy companies that will fuel our future.
Now, the third way to reduce carbon pollution is to waste less energy — in our cars, our homes, our businesses. The fuel standards we set over the past few years mean that by the middle of the next decade, the cars and trucks we buy will go twice as far on a gallon of gas. That means you’ll have to fill up half as often; we’ll all reduce carbon pollution. And we built on that success by setting the first-ever standards for heavy-duty trucks and buses and vans. And in the coming months, we’ll partner with truck makers to do it again for the next generation of vehicles.
Meanwhile, the energy we use in our homes and our businesses and our factories, our schools, our hospitals — that’s responsible for about one-third of our greenhouse gases. The good news is simple upgrades don’t just cut that pollution; they put people to work — manufacturing and installing smarter lights and windows and sensors and appliances. And the savings show up in our electricity bills every month — forever. That’s why we’ve set new energy standards for appliances like refrigerators and dishwashers. And today, our businesses are building better ones that will also cut carbon pollution and cut consumers’ electricity bills by hundreds of billions of dollars.
That means, by the way, that our federal government also has to lead by example. I’m proud that federal agencies have reduced their greenhouse gas emissions by more than 15 percent since I took office. But we can do even better than that. So today, I’m setting a new goal: Your federal government will consume 20 percent of its electricity from renewable sources within the next seven years. We are going to set that goal.
We’ll also encourage private capital to get off the sidelines and get into these energy-saving investments. And by the end of the next decade, these combined efficiency standards for appliances and federal buildings will reduce carbon pollution by at least three billion tons. That’s an amount equal to what our entire energy sector emits in nearly half a year.
So I know these standards don’t sound all that sexy, but think of it this way: That’s the equivalent of planting 7.6 billion trees and letting them grow for 10 years — all while doing the dishes. It is a great deal and we need to be doing it.
So using less dirty energy, transitioning to cleaner sources of energy, wasting less energy through our economy is where we need to go. And this plan will get us there faster. But I want to be honest — this will not get us there overnight. The hard truth is carbon pollution has built up in our atmosphere for decades now. And even if we Americans do our part, the planet will slowly keep warming for some time to come. The seas will slowly keep rising and storms will get more severe, based on the science. It’s like tapping the brakes of a car before you come to a complete stop and then can shift into reverse. It’s going to take time for carbon emissions to stabilize.
So in the meantime, we’re going to need to get prepared. And that’s why this plan will also protect critical sectors of our economy and prepare the United States for the impacts of climate change that we cannot avoid. States and cities across the country are already taking it upon themselves to get ready. Miami Beach is hardening its water supply against seeping saltwater. We’re partnering with the state of Florida to restore Florida’s natural clean water delivery system — the Everglades.
The overwhelmingly Republican legislature in Texas voted to spend money on a new water development bank as a long-running drought cost jobs and forced a town to truck in water from the outside.
New York City is fortifying its 520 miles of coastline as an insurance policy against more frequent and costly storms. And what we’ve learned from Hurricane Sandy and other disasters is that we’ve got to build smarter, more resilient infrastructure that can protect our homes and businesses, and withstand more powerful storms. That means stronger seawalls, natural barriers, hardened power grids, hardened water systems, hardened fuel supplies.
So the budget I sent Congress includes funding to support communities that build these projects, and this plan directs federal agencies to make sure that any new project funded with taxpayer dollars is built to withstand increased flood risks.
And we’ll partner with communities seeking help to prepare for droughts and floods, reduce the risk of wildfires, protect the dunes and wetlands that pull double duty as green space and as natural storm barriers. And we’ll also open our climate data and NASA climate imagery to the public, to make sure that cities and states assess risk under different climate scenarios, so that we don’t waste money building structures that don’t withstand the next storm.
So that’s what my administration will do to support the work already underway across America, not only to cut carbon pollution, but also to protect ourselves from climate change. But as I think everybody here understands, no nation can solve this challenge alone — not even one as powerful as ours. And that’s why the final part of our plan calls on America to lead — lead international efforts to combat a changing climate.
And make no mistake — the world still looks to America to lead. When I spoke to young people in Turkey a few years ago, the first question I got wasn’t about the challenges that part of the world faces. It was about the climate challenge that we all face, and America’s role in addressing it. And it was a fair question, because as the world’s largest economy and second-largest carbon emitter, as a country with unsurpassed ability to drive innovation and scientific breakthroughs, as the country that people around the world continue to look to in times of crisis, we’ve got a vital role to play. We can’t stand on the sidelines. We’ve got a unique responsibility. And the steps that I’ve outlined today prove that we’re willing to meet that responsibility.
Though all America’s carbon pollution fell last year, global carbon pollution rose to a record high. That’s a problem. Developing countries are using more and more energy, and tens of millions of people entering a global middle class naturally want to buy cars and air-conditioners of their own, just like us. Can’t blame them for that. And when you have conversations with poor countries, they’ll say, well, you went through these stages of development — why can’t we?
But what we also have to recognize is these same countries are also more vulnerable to the effects of climate change than we are. They don’t just have as much to lose, they probably have more to lose.
Developing nations with some of the fastest-rising levels of carbon pollution are going to have to take action to meet this challenge alongside us. They’re watching what we do, but we’ve got to make sure that they’re stepping up to the plate as well. We compete for business with them, but we also share a planet. And we have to all shoulder the responsibility for keeping the planet habitable, or we’re going to suffer the consequences — together.
So to help more countries transitioning to cleaner sources of energy and to help them do it faster, we’re going to partner with our private sector to apply private sector technological know-how in countries that transition to natural gas. We’ve mobilized billions of dollars in private capital for clean energy projects around the world.
Today, I’m calling for an end of public financing for new coal plants overseas — unless they deploy carbon-capture technologies, or there’s no other viable way for the poorest countries to generate electricity. And I urge other countries to join this effort.
And I’m directing my administration to launch negotiations toward global free trade in environmental goods and services, including clean energy technology, to help more countries skip past the dirty phase of development and join a global low-carbon economy. They don’t have to repeat all the same mistakes that we made.
We’ve also intensified our climate cooperation with major emerging economies like India and Brazil, and China — the world’s largest emitter. So, for example, earlier this month, President Xi of China and I reached an important agreement to jointly phase down our production and consumption of dangerous hydrofluorocarbons, and we intend to take more steps together in the months to come. It will make a difference. It’s a significant step in the reduction of carbon emissions.
And finally, my administration will redouble our efforts to engage our international partners in reaching a new global agreement to reduce carbon pollution through concrete action.
Four years ago, in Copenhagen, every major country agreed, for the first time, to limit carbon pollution by 2020. Two years ago, we decided to forge a new agreement beyond 2020 that would apply to all countries, not just developed countries.
What we need is an agreement that’s ambitious — because that’s what the scale of the challenge demands. We need an inclusive agreement — because every country has to play its part. And we need an agreement that’s flexible — because different nations have different needs. And if we can come together and get this right, we can define a sustainable future for your generation.
So that’s my plan. The actions I’ve announced today should send a strong signal to the world that America intends to take bold action to reduce carbon pollution. We will continue to lead by the power of our example, because that’s what the United States of America has always done.
I am convinced this is the fight America can, and will, lead in the 21st century. And I’m convinced this is a fight that America must lead. But it will require all of us to do our part.
We’ll need scientists to design new fuels, and we’ll need farmers to grow new fuels. We’ll need engineers to devise new technologies, and we’ll need businesses to make and sell those technologies. We’ll need workers to operate assembly lines that hum with high-tech, zero-carbon components, but we’ll also need builders to hammer into place the foundations for a new clean energy era.
We’re going to need to give special care to people and communities that are unsettled by this transition — not just here in the United States but around the world. And those of us in positions of responsibility, we’ll need to be less concerned with the judgment of special interests and well-connected donors, and more concerned with the judgment of posterity. Because you and your children, and your children’s children, will have to live with the consequences of our decisions.
As I said before, climate change has become a partisan issue, but it hasn’t always been. It wasn’t that long ago that Republicans led the way on new and innovative policies to tackle these issues. Richard Nixon opened the EPA. George H.W. Bush declared — first U.S. President to declare — “human activities are changing the atmosphere in unexpected and unprecedented ways.”
Someone who never shies away from a challenge, John McCain, introduced a market-based cap-and-trade bill to slow carbon pollution.
The woman that I’ve chosen to head up the EPA, Gina McCarthy, she’s worked — she’s terrific. Gina has worked for the EPA in my administration, but she’s also worked for five Republican governors. She’s got a long track record of working with industry and business leaders to forge common-sense solutions. Unfortunately, she’s being held up in the Senate. She’s been held up for months, forced to jump through hoops no Cabinet nominee should ever have to — not because she lacks qualifications, but because there are too many in the Republican Party right now who think that the Environmental Protection Agency has no business protecting our environment from carbon pollution. The Senate should confirm her without any further obstruction or delay.
But more broadly, we’ve got to move beyond partisan politics on this issue. I want to be clear — I am willing to work with anybody — Republicans, Democrats, independents, libertarians, greens — anybody — to combat this threat on behalf of our kids. I am open to all sorts of new ideas, maybe better ideas, to make sure that we deal with climate change in a way that promotes jobs and growth.
Nobody has a monopoly on what is a very hard problem, but I don’t have much patience for anyone who denies that this challenge is real. We don’t have time for a meeting of the Flat Earth Society. Sticking your head in the sand might make you feel safer, but it’s not going to protect you from the coming storm. And ultimately, we will be judged as a people, and as a society, and as a country on where we go from here.
Our founders believed that those of us in positions of power are elected not just to serve as custodians of the present, but as caretakers of the future. And they charged us to make decisions with an eye on a longer horizon than the arc of our own political careers. That’s what the American people expect. That’s what they deserve.
And someday, our children, and our children’s children, will look at us in the eye and they’ll ask us, did we do all that we could when we had the chance to deal with this problem and leave them a cleaner, safer, more stable world? And I want to be able to say, yes, we did. Don’t you want that?
Americans are not a people who look backwards; we’re a people who look forward. We’re not a people who fear what the future holds; we shape it. What we need in this fight are citizens who will stand up, and speak up, and compel us to do what this moment demands.
Understand this is not just a job for politicians. So I’m going to need all of you to educate your classmates, your colleagues, your parents, your friends. Tell them what’s at stake. Speak up at town halls, church groups, PTA meetings. Push back on misinformation. Speak up for the facts. Broaden the circle of those who are willing to stand up for our future.
Convince those in power to reduce our carbon pollution. Push your own communities to adopt smarter practices. Invest. Divest. Remind folks there’s no contradiction between a sound environment and strong economic growth. And remind everyone who represents you at every level of government that sheltering future generations against the ravages of climate change is a prerequisite for your vote. Make yourself heard on this issue.
I understand the politics will be tough. The challenge we must accept will not reward us with a clear moment of victory. There’s no gathering army to defeat. There’s no peace treaty to sign. When President Kennedy said we’d go to the moon within the decade, we knew we’d build a spaceship and we’d meet the goal. Our progress here will be measured differently — in crises averted, in a planet preserved. But can we imagine a more worthy goal? For while we may not live to see the full realization of our ambition, we will have the satisfaction of knowing that the world we leave to our children will be better off for what we did.
“It makes you realize,” that astronaut said all those years ago, “just what you have back there on Earth.” And that image in the photograph, that bright blue ball rising over the moon’s surface, containing everything we hold dear — the laughter of children, a quiet sunset, all the hopes and dreams of posterity — that’s what’s at stake. That’s what we’re fighting for. And if we remember that, I’m absolutely sure we’ll succeed.
Thank you. God bless you. God bless the United States of America.
17. Pepin County Board Votes to Protect Shore Strip Along Wisconsin Side of Lake Pepin from Frac Sand Mining
A 10-mile ribbon of popular bluff land on the Wisconsin side of Lake Pepin will be off limits to frac sand development under an unprecedented ordinance approved Wednesday night by the Pepin County Board.
“This is fabulous because it really protects all of the area of Lake Pepin in Pepin County. It’s a huge victory for us,” said Mary Logue, who was among the residents who pushed for the frac-free zone. “We’re really hoping it will be a template for other cities, villages and counties along the Mississippi that are fighting this.”
No Minnesota or Wisconsin county has flatly banned frac sand companies from operating in a defined territory. The Pepin County ordinance, which passed on a 9-3 vote, drew criticism from mining proponents and some County Board members, but a united core of residents around the villages of Pepin and Stockholm pushed for the frac-free zone on the premise that industrial sand projects would destroy the area’s natural endowments, wreck property values and impair the bedrock tourism trade.
“You would destroy fishing, boating, overnight camping and everything that goes with it,” said Pepin County Board Supervisor Bill Mavity, a lawyer and former Minneapolis police officer.
But Mark Krumenacher, who works for a company that sells services to a variety of mining industries, said other Lake Pepin communities in neighboring Pierce County have prospered from sand mining. The village of Maiden Rock, for instance, has long had an underground industrial sand mine.
“Tourism and quality of life clearly has not diminished in those communities, or in Stockholm and Pepin, during the period of industrial sand mining,” Krumenacher wrote this week to the County Board.
The ordinance bucks an industry that has rolled into a powerful position in Wisconsin over the past four years. The state holds vast deposits of uniquely formed silica sand needed by oil and gas drillers in other states as part of a national boom in hydraulic fracturing to recover crude and natural gas
The ordinance bucks an industry that has rolled into a powerful position in Wisconsin and Minnesota over the past four years. The two states hold vast deposits of uniquely formed silica sand needed by oil and gas drillers in other states as part of a national boom in hydraulic fracturing to recover crude and natural gas.
Mavity worked with Lake Pepin Partners in Preservation, a civic group, to rally local support for the ordinance, which was proposed after a frac sand group attempted unsuccessfully to build a processing plant and barge-loading terminal on a corner of the lake.
He said the zoning measure prohibits any kind of frac sand operation in a swath from the shoreline to the top of the area’s steep sandstone outcroppings. The ordinance is supported by the Wisconsin Mississippi Parkway Commission as a way to protect that portion of the Great River Road, which is a National Scenic Byway.
The two villages and two townships affected by the ordinance had already voted in support of it.
While Minnesota has fewer than 10 operating frac sand mines, additional mines and processing sites are being permitted in the wake of industry victories at the state Legislature this year. In Wisconsin, frac sand mining and processing has exploded from a handful of facilities three years ago to a nation-leading industry of 105 mines and 65 processing sites.
Tony Kennedy • 612-673-4213
10. U. S. Department of Agriculture Funded Research on Global Warming
Wisconsin State Journal Editorial
Published May 5, 2013
“Research to the rescue”
Federal investment in university research can help agriculture face the challenge of global warming.
On his trip to Wisconsin last week, U.S. Agriculture Secretary Tom Vilsack announced a prime example of the kind of smart investment the federal government should make to confront climate change and support the economy.
UW-Madison and six other universities are to share a $9.9 million grant for a five-year research project aimed at reducing the dairy industry’s greenhouse gas emissions. The project is especially important to Wisconsin, where the dairy industry contributes more than $26 billion a year to the state’s economy. Climate change is a threat to the industry and, consequently, a threat to Wisconsin’s economy.
In the long term, climate change puts Wisconsin at risk of becoming less desirable as a location for dairying. But of more immediate concern is the dairy industry’s contribution to climate change.
The industry produces 2 percent of U.S. greenhouse gas emissions, which tend to keep more heat in the atmosphere. Customers, including Wal-Mart, are pressuring the industry to cut emissions. Furthermore, the prospect of federal regulation looms.
In response, the industry has pledged to cut emissions by 25 percent in the next seven years.
Just as climate change poses a threat, the response poses an opportunity. By finding ways to cut emissions, the industry can improve efficiency, which would boost profits.
University research on new technologies and strategies can play a central role in helping the industry meet its challenges and take advantage of its opportunities, as a look through history demonstrates.
Wisconsin was a wheat-growing state in the 1800s. But when wheat farming declined, University of Wisconsin research helped the state become “America’s Dairyland.” During the Dust Bowl on the Great Plains in the 1930s, university research found farming methods that cut down on wind erosion. After the Dust Bowl, university research helped produce higher-yielding hybrid crops.
No doubt, some wag will ridicule the USDA grant as a waste of taxpayer money on a study of manure, which indeed will be a part of the research. But while these are times to control government spending, these are also times to invest in the country’s future.
Investing in research to combat climate change and improve the dairy industry is the right priority.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Published in Wisconsin State Journal on May 19, 2013
Question Asked: Is research key to helping Wisconsin farmers deal with climate change?
“Let fossil fuel industry fund research”
I have reservations about this federally funded university study on the dairy industry reducing its greenhouse gas emissions.
Industries knew the importance of stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at the United Nations’ 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. President George H. W. Bush signed an agreement at the summit.
Besides being too little in the fight against global warming, UW-Madison’s research grant seems too late.
Unfortunately for us, few U.S. industries took the threat of climate change seriously enough to begin researching ways to reduce emissions 20 years ago.
Now that we are beginning to experience effects of the increasingly warmer atmosphere — rising sea levels, higher temperatures, melting polar ice caps — the Department of Agriculture finally decides it’s time to fund research into reducing dairy’s contribution to the “problem” (catastrophe) of global warming.
Who should fund the studies? Global warming scientists have pinpointed the majority of this problem to fossil fuel burning. That industry should be tapped to fund the lion’s share of funding, not the American taxpayers.
— Michael Neuman, Madison
“Let farmers lead the way”
Of course research is key to helping Wisconsin farmers deal with climate change. And not just farmers — research helps all of us.
When humanity began large-scale fossil fuel burning by industrializing, we unintentionally began a planetary experiment on the effects of adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
We didn’t realize then we might threaten our survival, but thanks to scientists we understand it now. The vast majority of climate scientists agree climate change is real, primarily human-induced and dangerous if unchecked.
So I’m delighted the university will be researching how to lower emissions in the dairy industry. But research is just the beginning. We must also act on what we learn. We need good federal climate policy.
The best idea I’ve seen, based on economic research, is a steadily-rising fee on carbon-based fuels so they reflect their true cost to society, with a return of the revenue to households to cushion the impact of rising prices.
Both liberal and conservative economists have concluded this is the most effective way to stimulate the change we need in our energy system. Many opportunities will arise as we make this change, and I would love to see our farmers lead the way.
— Madeleine Para, Madison
5. “An Inconvenient Truth” – the Movie – and Photo Comic of Earth’s Warming
“In 39 years, I have never written these words in a movie review, but here they are. You owe it to yourself to see this film.”
– Roger Ebert
“It doesn’t matter whether you’re a Republican or Democrat, liberal or conservative … your mind will be changed in a nanosecond.”
– Roger Friedman, FOXNEWS.com
Here you can watch An Inconvenient Truth.
Here is a photo comic about global warming:





Recent Comments